Abstract
In 2015, a germline copy number variation of chromosome 14 (CNVdup14) including ATG2B and GSKIP genes was described as a predisposition genetic factor responsible of familial myeloproliferative neoplasms from French West Indies (Saliba et al, Nat Gen 2015), frequently progressing to AML. In this study, we looked at the presence of this CNVdup14 in a cohort of Caribbean islands patients (pts) with non-secondary aggressive hematological malignancies (HM). We also studied the expression of ATG2B and GSKIP genes in a cohort of acquired AML pts.
This is a retrospective multicenter study of adults Caribbean islands pts treated at Gustave Roussy Cancer Center (Villejuif, France) and at the French West Indian hospitals (Martinique and Guadeloupe) between May 2000 and May 2018. We included pts with AML, acute undifferentiated leukemia (AUL), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoblastic lymphoma (LL). Pts with personal history of myeloproliferative or myelodysplastic syndromes before the onset of aggressive HM were not included in this study. The presence of the CNVdup14 was carried out by PCR analyses in all the pts.
For the second part of the study, expression of ATG2B and GSKIP genes were assessed in newly diagnosed de novo AML pts with normal karyotype or trisomy 8 (samples from the GOELAMSTHEQUE) by quantitative RT-PCR and expressed as relative expression PPIA/HPRT/H2A.Z.
One hundred pts were analyzed. Median age was 52 years (IQ 40-62) with male predominance (61%). Fifty eight pts came from Martinique, 42 pts from the rest of the Caribbean islands (including 28, 4, 3, 2 pts from Guadeloupe, Haiti, Saint Martin, Dominican Republic, respectively). Seventy eight pts had AML. Among them, according to revised MRC cytogenetic classification, 11 (14%) were favorable, 47 (60%) intermediate and 20 (26%) adverse. Seventeen pts had ALL, 3 LL, and 2 AUL. On the entire cohort, all except nine pts were treated with intensive chemotherapy, 80 reached complete remission, 29 relapsed, 46 pts died. Thirty two pts received hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
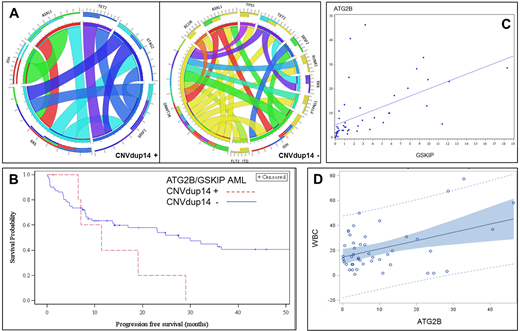
Six pts were positive for the CNVdup14 by PCR (confirmed by SNP array in the 5 pts with leftover DNA available). All had an AML (no pts with favorable AML) and were originated from Martinique. These pts represented 14% of the 43 AML from Martinique in our cohort (17% if we excluded favorable AML). One was known to be part of an ATG2B/GSKIP family, 2 pts had no familial history of myeloid malignancies and 2 new families were discovered. Median white blood cell, hemoglobin and platelets counts were 17.7 G/l (IQ 6.7-48), 8.15 g/dl (6.9-9.7) and 58 G/l (20-132), respectively. Median age at AML diagnosis was 49 years (34-55), 3/6 (50%) had extramedullary localization compared to 11/78 (14%) for others AML pts. Karyotype was normal for 4, or showed a monosomy 7 for 2 pts. NGS panel showed distinct abnormalities compared to the entire cohort (Fig A). None had JAK2, MPL, CALR, P53, RUNX1, DNMT3A, FLT3-ITD mutations. All harbored an epigenetic and/or spliceosome mutation (IDH n=3, TET2 n=3, ASLX1 n=3, SRSF2 n=3). Five out of the six pts received intensive treatment and 4 achieved complete remission. Two received HSCT, 2 relapsed and 4 died.
Median overall survival (OS) of the entire cohort was 35.7 months (22.5-89.5) and progression free survival (PFS) 27.6 months (15.6 -56.1). As CNVdup14 pts had AML only, we next evaluated survival according to the predisposition status in the AML cohort. Pts with CNVdup14 had a median OS and PFS of 19 (6.5-29) and 11.4 (6.5-29) months, respectively, compared with 52.6 (22.9-100.2) and 30 months (15.6-60) in CNV wild-type counterparts (PFS Fig B).
We next evaluated ATG2B and GSKIP expression in a cohort of 46 random de novo AML pts (GOELAMS-LAM-IR-2006 multicenter trial). Median expression of ATG2B and GSKIP were 4.8 (2.6-12.9) and 5.3 (0.3-5.1) respectively. No CNVdup14 was detected. Interestingly we found a correlation between the two genes expression (Pearson Correlation Coefficients 0.55 and linear regression p< 0.001, Fig C). Expression of ATG2B and GSKIP was also correlated with leukocytosis (p=0.003 and p=0.07) (Fig D). We found no impact on OS and PFS.
For the first time, we described a high percentage of the germline CNVdup14 in de novo AML pts from Martinique (14%). Moreover evaluation of ATG2B and GSKIP expression suggested that the role of theses 2 genes in leukemogenesis is not limited to pts with the CNVdup14.
de Botton:Agios: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Benabelali:CERBA laboratory: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal